reading-notes
TDD with Python
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is a strategy to think (and write!) tests first.
For Example:
if you want to detect the gender of client and you find API that work on this idea and all thing will be fine ,But with TDD we need to think about tests first ,so in this case the simplest test is : given a name, return a gender.
we are going to write a test just to check !!
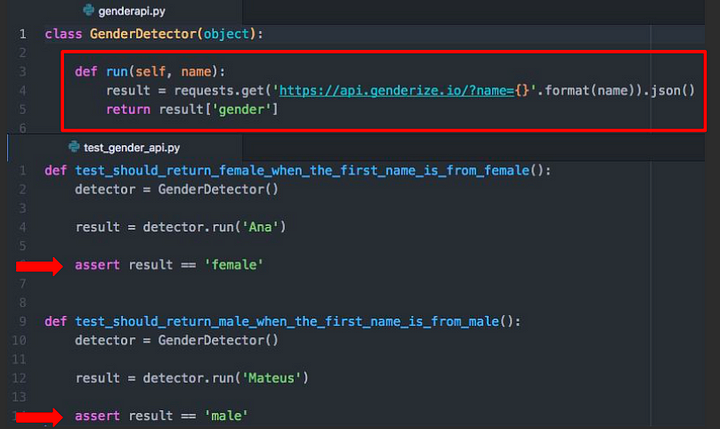
Hints!!
1.Test file name should follow the same name of module name. For instance, if our module is gender.py, our test name should be test_gender.py. (It’s ideal to separate the tests folder from production code ).
2.The structure. using the AAA: Arrange (organize the data needed to execute), Act (exercise the behaviour) and Assert (check if the result is the same as expecting).
What does if name == “main”: do ?
1.Firstly , python interpreter reads source file and define few special variables/global variables.
2.After that, if the python interpreter is running that module (the source file) as the main program, it sets the special name variable to have a value “main”.
3.If this file is being imported from another module, name will be set to the module’s name,so the if statement will being false and all lines of code under it won’t be excuted.
why do we need it ?
*we need it when we want to import piece of code from other module (not all lines) ,we can put the lines that not needed under the if statement ,thats it !*
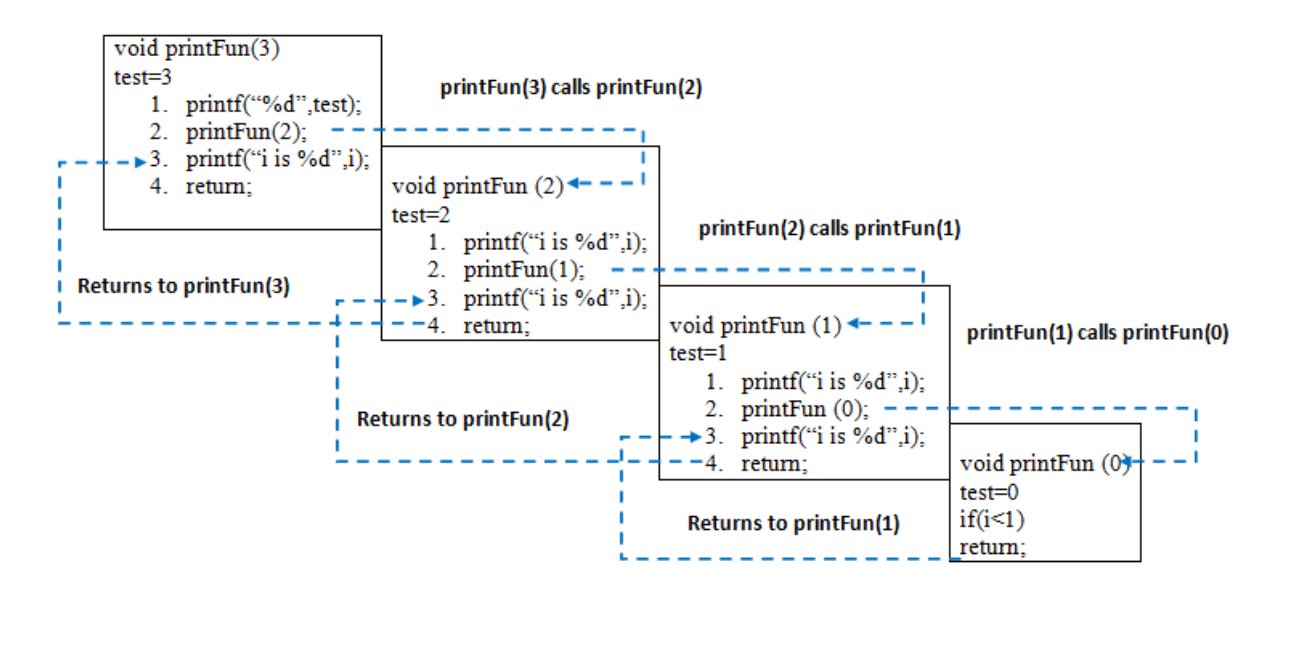
Recursion
The process in which a function calls itself directly or indirectly,A recursive function solves a particular problem by calling a copy of itself and solving smaller subproblems of the original problems.
Need of Recursion
Recursion is technique that we can reduce the length of our code and make it easier to read and write. A task that can be defined with its similar subtask, recursion is one of the best solutions for it.
Base Condition
The idea is to represent a problem in terms of one or more smaller problems, and add one or more base conditions that stop the recursion. For example, we compute factorial n if we know the factorial of (n-1). The base case for factorial would be n = 0. We return 1 when n = 0.
Direct and indirect recursion
1.A function fun is called direct recursive if it calls the same function fun 2.A function fun is called indirect recursive if it calls another function say fun_new and fun_new calls fun
Tailed and non-tailed recursion
A recursive function is tail recursive when a recursive call is the last thing executed by the function
Advantages and Disadvantages of recursive programming over iterative programming
| Advantages | DisAdvantages |
|---|---|
| provides a clean and simple way to write code | has greater space requirements |
| Some problems are inherently recursive | codes are difficult to understand, hence extra care to be practiced |