reading-notes
What are Design Patterns
*Developers have noticed that they seemed to be approaching problems in similar ways in a bunch of different software’s, then they decided that it would be pretty useful to be able to talk about those approaches using a common vocabulary* *Thus they figured out general versions of these common practices and gave them names like “Adapter” and “Singleton.”*
A design pattern is only a description or template for how to solve a problem!
1. Programming Paradigms: A way to classify programming languages based on their coding styles and features.
2. Architectural Patterns: Reusable solution to a commonly occurring problem in software architecture within a given context.
3. Design Principles: Represent a set of guidelines that help developers to avoid having a bad design.
4. Design Patterns: Reusable solution to a commonly occurring problem in software design within a given context. and has three major types:
#### Creational Patterns: Creational patterns provide ways to instantiate single or groups of objects. Making it easier to create objects in a way that suits the situation.
1.Factory Method. The factory pattern is used to replace class constructors, abstracting the process of object generation so that the type of the object instantiated can be determined at run-time.
2.Singleton. The singleton pattern ensures that only one object of a particular class is ever created. All further references to objects of the singleton class refer to the same underlying instance.
3.Abstract Factory. The abstract factory pattern is used to provide a client with a set of related or dependent objects. The “family” of objects created by the factory are determined at run-time.
#### Structural Patterns:Structural patterns provide a manner to define relationships between classes or objects. Making it easier for these entities to work together.
1.Facade. The facade pattern is used to define a simplified interface to a more complex subsystem.
2.Adapter. The adapter pattern is used to provide a link between two otherwise incompatible types by wrapping the “adaptee” with a class that supports the interface required by the client.
3.Decorator. The decorator pattern is used to extend or alter the functionality of objects at run-time by wrapping them in an object of a decorator class. This provides a flexible alternative to using inheritance to modify behavior.
#### Behavioral Patterns:Behavioral patterns define manners of communication between classes and objects. Making it easier and more flexible for these entities to communicate.
1.Observer. The observer pattern is used to allow an object to publish changes to its state. Other objects subscribe to be immediately notified of any changes.
2.Mediator. The mediator pattern is used to reduce coupling between classes that communicate with each other. Instead of classes communicating directly, and thus requiring knowledge of their implementation, the classes send messages via a mediator object.
3.Chain of Responsibility. The chain of responsibility pattern is used to process varied requests, each of which may be dealt with by a different handler.
## Risk Analysis
### Why use Risk Analysis?
*In any software, using risk analysis at the beginning of a project highlights the potential problem areas. After knowing about the risk areas, it helps the developers and managers to mitigate the risks.*
Risk Identification
There are different sets of risks included in the risk identification process. Those are as follows:
1.Business Risks: This risk is the most common risk associated with our topic. It is the risk that may come from your company or your customer, not from your project.
2.Testing Risks: You should be well acquainted with the platform you are working on, along with the software testing tools being used.
3.Premature Release Risk: a fair amount of knowledge to analyze the risk associated with releasing unsatisfactory or untested software is required
4.Software Risks: You should be well versed with the risks associated with the software development process.
Risk Assessment
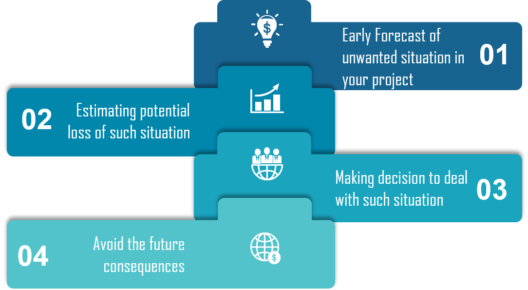
Perspective of Risk Assessment
There are three perspectives of Risk Assessment:
1.Effect – To assess risk by Effect. In case you identify a condition, event or action and try to determine its impact.
2.Cause – To assess risk by Cause is opposite of by Effect. Initialize scanning the problem and reach to the point that could be the most probable reason behind that.
3.Likelihood – To assess risk by Likelihood is to say that there is a probability that a requirement won’t be satisfied.
How to perform Risk Analysis?
There are three steps:
1.Searching the risk
2.Analyzing the impact of each individual risk
3.Measures for the risk identified
Dependency Injection
*is a technique whereby one object (or static method) supplies the dependencies of another object. A dependency is an object that can be used (a service),So, transferring the task of creating the object to someone else and directly using the dependency is called dependency injection.*
There are basically three types of dependency injection:
1.constructor injection: the dependencies are provided through a class constructor.
2.setter injection: the client exposes a setter method that the injector uses to inject the dependency.
3.interface injection: the dependency provides an injector method that will inject the dependency into any client passed to it. Clients must implement an interface that exposes a setter method that accepts the dependency.
Libraries and Frameworks that implement DI
Spring (Java) Google Guice (Java) Dagger (Java and Android) Castle Windsor (.NET) Unity(.NET)