reading-notes
Data structures
*A data structure is a specialized format for organizing, processing, retrieving and storing data. There are several basic and advanced types of data structures, all designed to arrange data to suit a specific purpose. Data structures make it easy for users to access and work with the data they need in appropriate ways*
Why are data structures important?
_*Data structures are the building blocks for more sophisticated applications. They are designed by composing data elements into a logical unit representing an abstract data type that has relevance to the algorithm or application. An example of an abstract data type is a “customer name” that is composed of the character strings for “first name,” “middle name” and “last name.”
It is not only important to use data structures, but it is also important to choose the proper data structure for each task.*_
How are data structures used?
*Software engineers use algorithms that are tightly coupled with the data structures – such as lists, queues and mappings from one set of values to another. This approach can be fused in a variety of applications, including managing collections of records in a relational database and creating an index of those records using a data structure called a binary tree.*
Some examples of how data structures are used include the following:
1.Storing data. Data structures are used for efficient data persistence, such as specifying the collection of attributes and corresponding structures used to store records in a database management system.
2.Managing resources and services. Core operating system (OS) resources and services are enabled through the use of data structures such as linked lists for memory allocation, file directory management and file structure trees, as well as process scheduling queues.
3.Data exchange. Data structures define the organization of information shared between applications, such as TCP/IP packets.
4.Ordering and sorting. Data structures such as binary search trees – also known as an ordered or sorted binary tree – provide efficient methods of sorting objects, such as character strings used as tags.
5.Indexing. Even more sophisticated data structures such as B-trees are used to index objects, such as those stored in a database.
6.Searching. Indexes created using binary search trees, B-trees or hash tables speed the ability to find a specific sought-after item.
7.Scalability. Big data applications use data structures for allocating and managing data storage across distributed storage locations, ensuring scalability and performance.
Types of data structures
1.Array : An array stores a collection of items at adjoining memory locations. Items that are the same type are stored together so the position of each element can be calculated or retrieved easily by an index. Arrays can be fixed or flexible in length.
2.Stack. A stack stores a collection of items in the linear order that operations are applied. This order could be last in, first out (LIFO) or first in, first out (FIFO).
3.Queue. A queue stores a collection of items like a stack; however, the operation order can only be first in, first out.
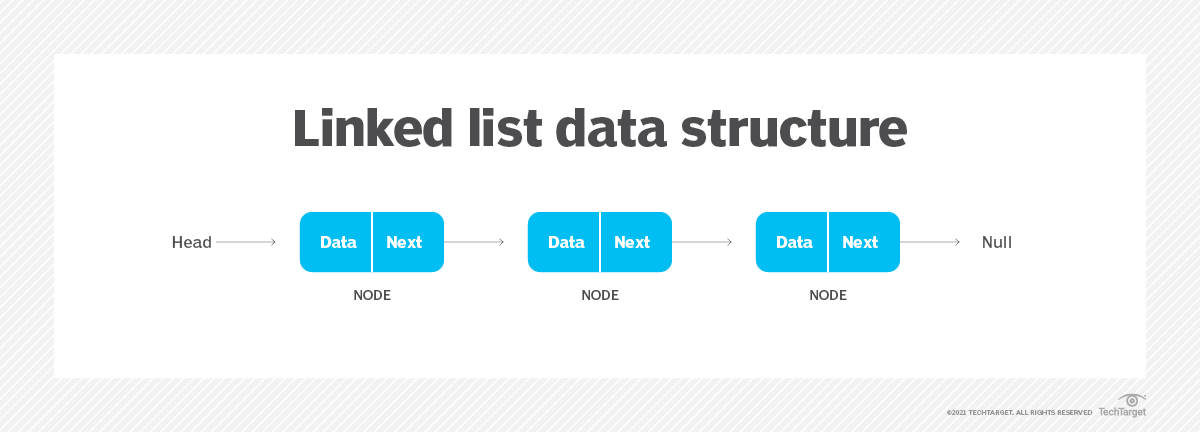
4.Linked list. A linked list stores a collection of items in a linear order. Each element, or node, in a linked list contains a data item, as well as a reference, or link, to the next item in the list.
5.Tree. A tree stores a collection of items in an abstract, hierarchical way. Each node is associated with a key value, with parent nodes linked to child nodes – or subnodes. There is one root node that is the ancestor of all the nodes in the tree.
6.Heap. A heap is a tree-based structure in which each parent node’s associated key value is greater than or equal to the key values of any of its children’s key values.
7.Graph. A graph stores a collection of items in a nonlinear fashion. Graphs are made up of a finite set of nodes, also known as vertices, and lines that connect them, also known as edges. These are useful for representing real-world systems such as computer networks.
8.Trie. A trie, also known as a keyword tree, is a data structure that stores strings as data items that can be organized in a visual graph.
9.Hash table. A hash table – also known as a hash map – stores a collection of items in an associative array that plots keys to values. A hash table uses a hash function to convert an index into an array of buckets that contain the desired data item.
Linked List
important points to be considered.
. Linked List contains a link element called first.
. Each link carries a data field(s) and a link field called next.
. Each link is linked with its next link using its next link.
. Last link carries a link as null to mark the end of the list.
Types of Linked List
-
Simple Linked List.
-
Doubly Linked List − Items can be navigated forward and backward.
-
Circular Linked List
Basic Operations
1.Insertion − Adds an element at the beginning of the list.
2.Deletion − Deletes an element at the beginning of the list.
3.Display − Displays the complete list.
4.Search − Searches an element using the given key.
5.Delete − Deletes an element using the given key.