reading-notes
Stacks and Queues
Stack:
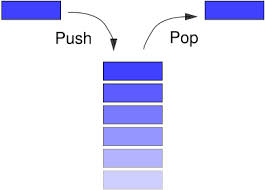
*In the pushdown stacks only two operations are allowed: push the item into the stack, and pop the item out of the stack. A stack is a limited access data structure elements can be added and removed from the stack only at the top. push adds an item to the top of the stack, pop removes the item from the top. A helpful analogy is to think of a stack of books; you can remove only the top book, also you can add a new book on the top.*
Queue:
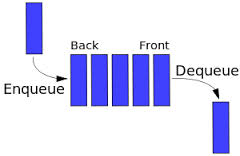
An excellent example of a queue is a line of students in the food court of the UC. New additions to a line made to the back of the queue, while removal (or serving) happens in the front. In the queue only two operations are allowed enqueue and dequeue. Enqueue means to insert an item into the back of the queue, dequeue means removing the front item. The picture demonstrates the FIFO access. The difference between stacks and queues is in removing. In a stack we remove the item the most recently added; in a queue, we remove the item the least recently added.
FIFO & LILO and LIFO & FILO
Queue: First In First Out (FIFO): The first object into a queue is the first object to leave the queue, used by a queue.
Stack: Last In First Out (LIFO): The last object into a stack is the first object to leave the stack, used by a stack
OR
Stack: First In Last Out (FILO): The first object or item in a stack is the last object or item to leave the stack.
Queue: Last In Last Out (LILO): The last object or item in a queue is the last object or item to leave the queue.
Stack Data Structure
LIFO Principle of Stack
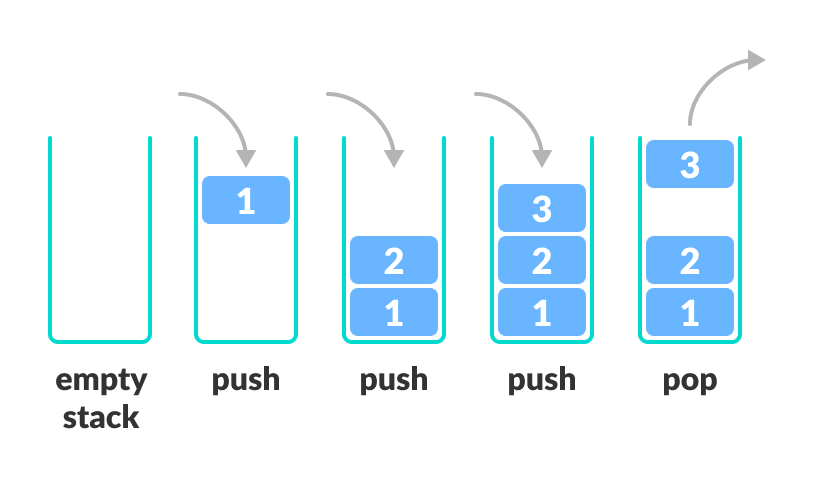
In programming terms, putting an item on top of the stack is called push and removing an item is called pop.
Basic Operations of Stack
1.Push: Add an element to the top of a stack
2.Pop: Remove an element from the top of a stack
3.IsEmpty: Check if the stack is empty
4.IsFull: Check if the stack is full
5.Peek: Get the value of the top element without removing it
Working of Stack Data Structure
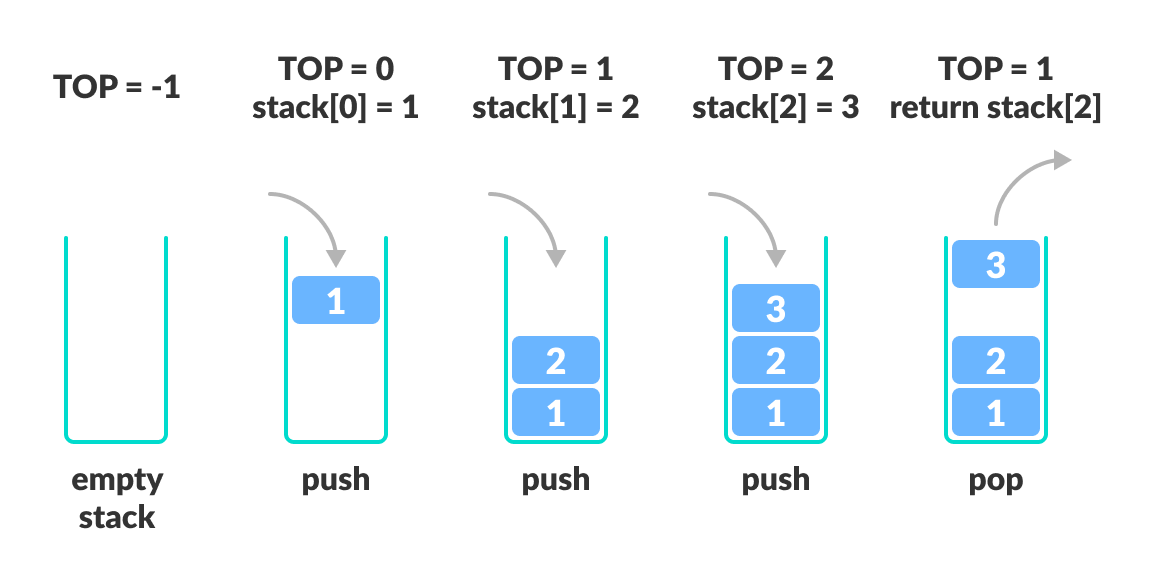
1.A pointer called TOP is used to keep track of the top element in the stack.
2.When initializing the stack, we set its value to -1 so that we can check if the stack is empty by comparing TOP == -1.
3.On pushing an element, we increase the value of TOP and place the new element in the position pointed to by TOP.
4.On popping an element, we return the element pointed to by TOP and reduce its value.
5.Before pushing, we check if the stack is already full.
6.Before popping, we check if the stack is already empty.
Stack Time Complexity
For the array-based implementation of a stack, the push and pop operations take constant time, i.e. O(1).
Applications of Stack Data Structure
The most common uses of a stack are: