reading-notes
Tree Data Structure
*A tree is a nonlinear hierarchical data structure that consists of nodes connected by edges*
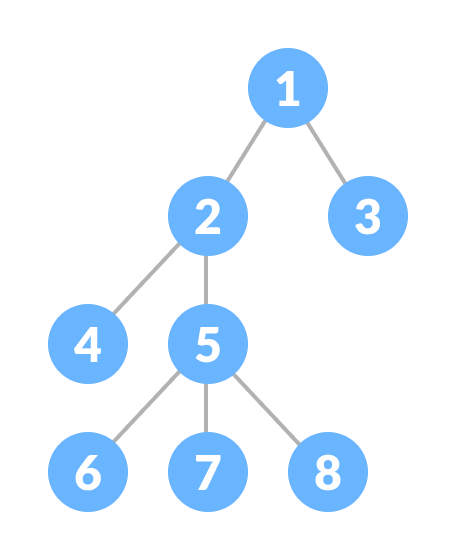
Why Tree Data Structure?
_*Other data structures such as arrays, linked list, stack, and queue are linear data structures that store data sequentially. In order to perform any operation in a linear data structure, the time complexity increases with the increase in the data size. But, it is not acceptable in today’s computational world.
Different tree data structures allow quicker and easier access to the data as it is a non-linear data structure.*_.
Tree Terminologies
- Node
A node is an entity that contains a key or value and pointers to its child nodes.
The last nodes of each path are called leaf nodes or external nodes that do not contain a link/pointer to child nodes.
The node having at least a child node is called an internal node.
- Edges
It is the link between any two nodes.
3.Root
It is the topmost node of a tree.
4.Height of a Node
The height of a node is the number of edges from the node to the deepest leaf (ie. the longest path from the node to a leaf node).
5.Depth of a Node
The depth of a node is the number of edges from the root to the node.
6.Height of a Tree
The height of a Tree is the height of the root node or the depth of the deepest node.
7.Degree of a Node
The degree of a node is the total number of branches of that node
8.Forest
A collection of disjoint trees is called a forest.
Types of Tree
.Binary Tree .Binary Search Tree .AVL Tree .B-Tree
Tree Applications
1.Binary Search Trees(BSTs) are used to quickly check whether an element is present in a set or not.
2.Heap is a kind of tree that is used for heap sort.
3.A modified version of a tree called Tries is used in modern routers to store routing information.
4.Most popular databases use B-Trees and T-Trees, which are variants of the tree structure we learned above to store their data Compilers use a syntax tree to validate the syntax of every program you write.
Binary Tree
A tree whose elements have at most two children is called a binary tree. Each element in a binary tree can have only two children. A node’s left child must have a value less than its parent’s value, and the node’s right child must have a value greater than its parent value.
implementation
we have created a node class and assigned a value to the node
node class
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
# left child
self.left = None
# right child
self.right = None
# node's value
self.data = data
insertion
The insert method compares the value of the node to the parent node and decides whether to add it as a left node or right node.
def insert(self, data):
if self.data:
if data < self.data:
if self.left is None:
self.left = Node(data)
else:
self.left.insert(data)
elif data > self.data:
if self.right is None:
self.right = Node(data)
else:
self.right.insert(data)
else:
self.data = data
searching
def findval(self, lkpval):
if lkpval < self.data:
if self.left is None:
return str(lkpval)+" is not Found"
return self.left.findval(lkpval)
elif lkpval > self.data:
if self.right is None:
return str(lkpval)+" is not Found"
return self.right.findval(lkpval)
else:
return str(self.data) + " is found"